# Formatting Drives
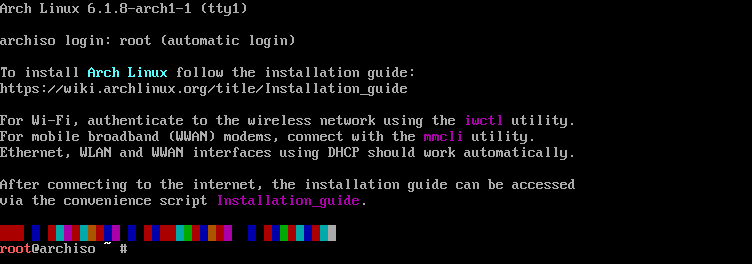
1. You should now be inside the Arch shell. Below is a screenshot of what it looks like.
2. With the command below, you can list all currently attached drives. In that list, there should at least be your main Hard Drive and your Flash Drive.
```bash
root@archiso ~ # lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
loop0 7:0 0 710.1M 1 loop /run/archiso/airootfs
sr0 11:0 1 824.3M 0 rom
vda 254:0 0 20G 0 disk
```
In my case, my Hard Drive I'll be installing Arch to is `vda` because I am in a Virtual Machine. Yours might be called `sda`, `nvme0n1p` or `hda`, depending on if you've installed an SSD, an NVMe SSD or an HDD respectively.
3. We are now going to format this drive using `cfdisk`. You can also format your drive with `fdisk`, but `cfdisk` has a simple to navigate interface.
```bash
root@archiso ~ # cfdisk /dev/vda
```
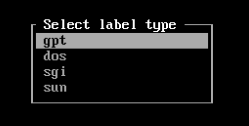
1. If your Hard Disk is empty, you're now going to be met with the following options. This will not show up if you've already partitioned your drive, like if you're coming from Windows, so if you see your partitions already, go to step 2.
[](https://wiki.sangelo.space/uploads/images/gallery/2023-02/WhWkfMgdUJSxYE8m-image-1676455005009.png)
Here, choose `gpt` (GUID Partition Table) for drives bigger than 2 TB and machines using UEFI and `dos` (Master Boot Record) otherwise. Once you come to this screen, you can skip the next step. [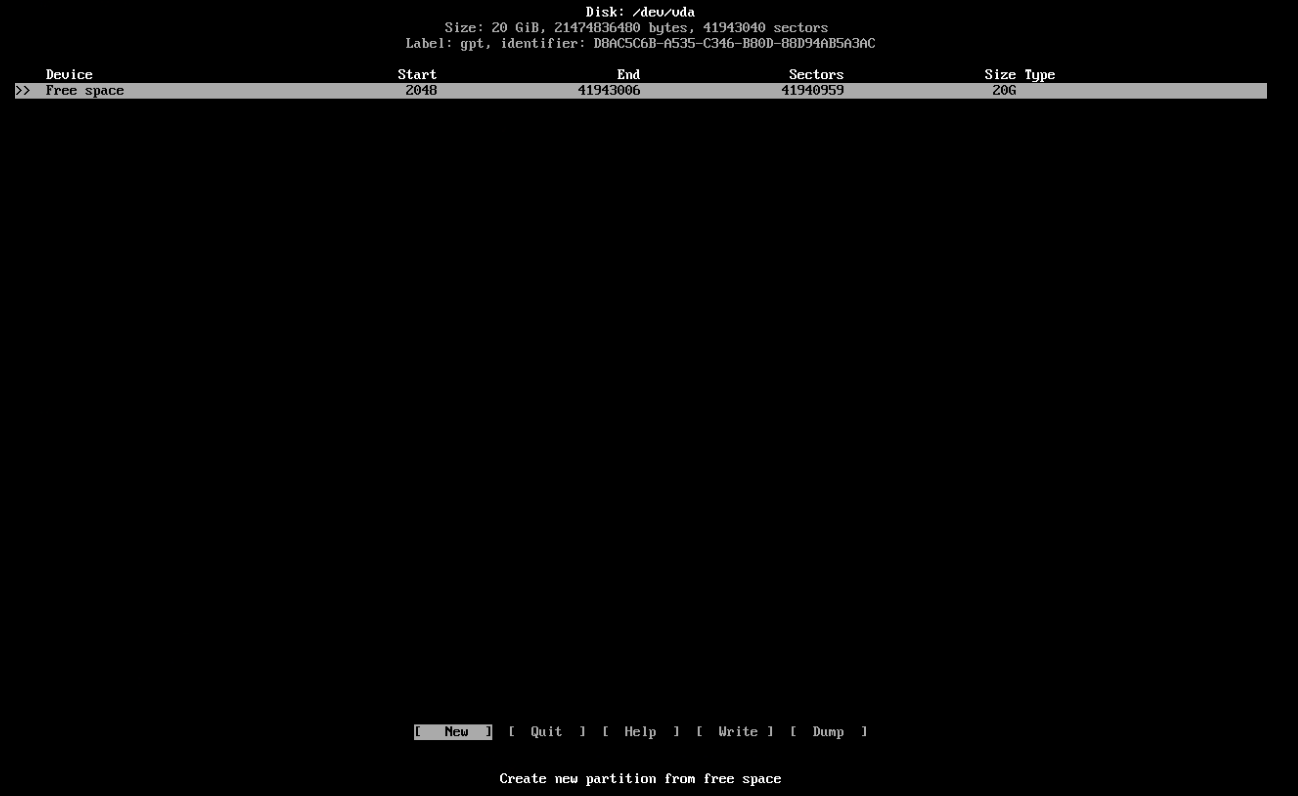](https://wiki.sangelo.space/uploads/images/gallery/2023-02/kUwH5NrC2yTZrqUj-image-1676455757531.png)
2. If you come from another operating system, you're going to have a few entries here. You can either remove all the partitions, or create new ones to install Arch into. To remove partitions, use your arrow keys to navigate to the delete option and hit enter for each partition you'd like to delete. [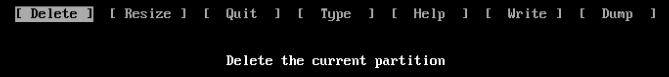](https://wiki.sangelo.space/uploads/images/gallery/2023-02/U1SzZVRhVV6QocUF-image-1676455934961.png)
3. Once you've got an empty slate, we can start creating all the necessary partitions. Create them in the order and sizes shown below.
| Partition | Size |
|---|
| Boot | 100M |
| Swap | Half your RAM |
| Root | The rest of your storage |
**Tip:** You can also create a Home partition now, if you want to be able to change distros without deleting your user data
Your Partitions should look something similar to this: [](https://wiki.sangelo.space/uploads/images/gallery/2023-02/kd4eAKY9V7UIRoPY-image-1676457605662.png)
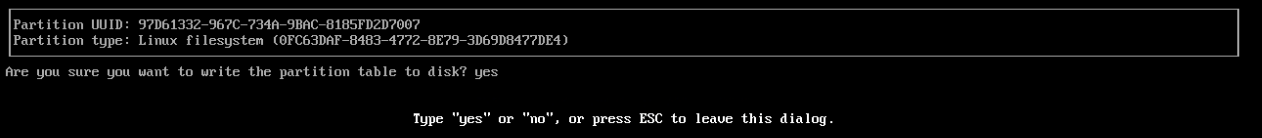
4. Once you're done partitioning your drive, you can go over to the Write option, hit enter, and confirm the partitioning process by typing `yes`. Then you can quit out of `cfdisk`.
**Danger!** This process will permanently delete any partitions you chose to delete. Double-check your partitioning scheme, so that you do not delete important data.
[](https://wiki.sangelo.space/uploads/images/gallery/2023-02/gc6CldVfat3HpbAc-image-1676457813219.png)
4. We can now properly format the drives. For that, we need to know how the new partitions are called. Run `lsblk` again. In the guide above, we created the partitions like in the table below, and `lsblk` reflects that.
| Partition | Name |
|---|
| Boot | /dev/vda1 |
| Swap | /dev/vda2 |
| Root | /dev/vda3 |
1. Let's first format the boot and root partitions with the following commands. Note that the boot partition has to be in FAT32, otherwise it won't be recognized:
```bash
#==> Important: replace /dev/vda with your drive!
root@archiso ~ # mkfs.fat -F 32 /dev/vda1 root@archiso ~ # mkfs.ext4 /dev/vda3
```
**Note:** You can also format your root partition to be in the BTRFS format, which allows snapshots. Just replace ext4 with btrfs in the command above.
2. Formatting the swap partition is a little different:
```bash
#==> Important: replace /dev/vda with your drive!
root@archiso ~ # mkswap /dev/vda2
```
You're done! You can now go to the next step of mounting the drives and installing Arch!